Combining analog and digital outputs with Android and Arduino. This tutorial will demonstrate the basic use of combined digital and analog outputs. The basic hardware is a hobby servo and two LEDs inside of an Android figure. The servo allows Andy Android to rotate 180 degrees.
For additional background information on interfacing Android with the real world, check out my other introductory tutorials:
Hardware
Parts needed:
-
Android Device (1.6+)
-
Hobby servo
-
2x LEDs
-
2x 330 ohm resistors
-
Breadboard
-
Power supply
-
Hook-up wire
-
Android ADK Board*
-
– OR –
-
Arduino compatible and USB Host shield
*Supported boards include:
Google ADK board, Freeduino ADK board , Seeed Studio ADK board, and DIY Drones ADK board
Assembly
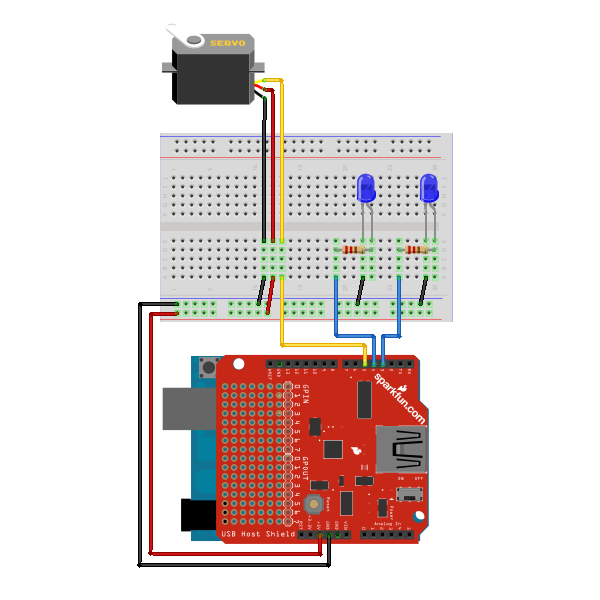
Connect the two LEDs to digital output pins 3 and 4, using a 330 ohm resistor for each in series to limit current. Connect the signal line of the servo to pin 5. Other pins can be used, as long as the servo signal line is capable of PWM (usually has a ~ symbol next to it on the Arduino board) and none interfere with the SPI lines connecting to the USB Host (10 -14 on most). Here is a diagram of the completed circuit (created with Fritzing):
Software
Arduino Firmware
Next, upload the Arduino sketch to the microcontroller. The sketch uses the Microbridge implementation by Niels Brouwers. Microbridge uses Android Debug Bridge (ABD) forwarding over TCP, rather than the official Google Android ADK. You can checkout the source for the Arduino sketch from Github, or just copy and paste the following into the Arduino IDE.
Android App
Finally, install the Android Demo application onto the device. You can either download the pre-built .apkor checkout the source from Github:
git clone git://github.com/mitchtech/android_adb_andy_android.git
Finally upload the app to the device (or browse to this page on the device and download the apk above). Connect the Android device to the USB Host board/shield, and start up the app.